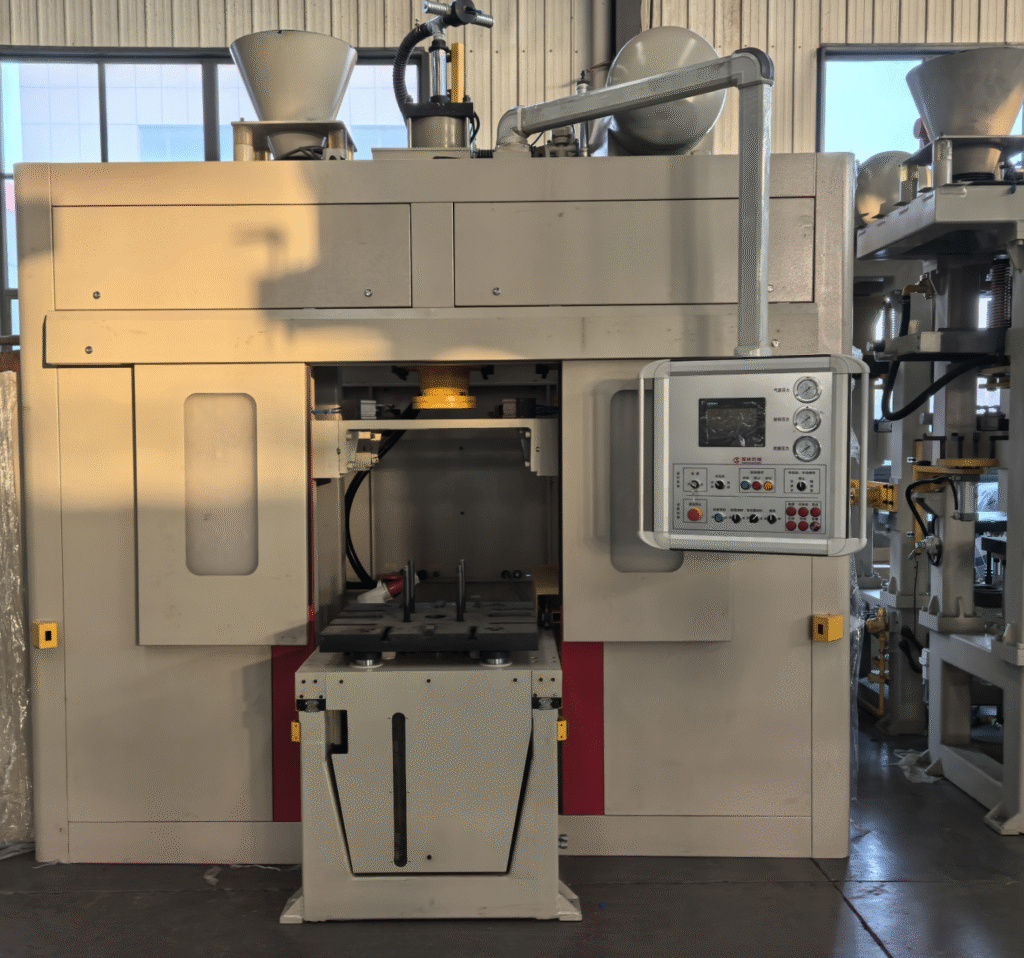
Confusion about shot blasters leads to poor choices, wasted costs, and inefficient cleaning. This guide simplifies Shot Blaster Types, tips, and tricks for success.
This guide demystifies shot blasters: explore mainstream Shot Blaster Types, essential Selection Tips, efficiency-boosting Efficiency Tricks, and maintenance insights to extend service life.
Dive into detailed, practical advice to master shot blasters from selection to long-term use.

What are the mainstream shot blaster types and their key uses?
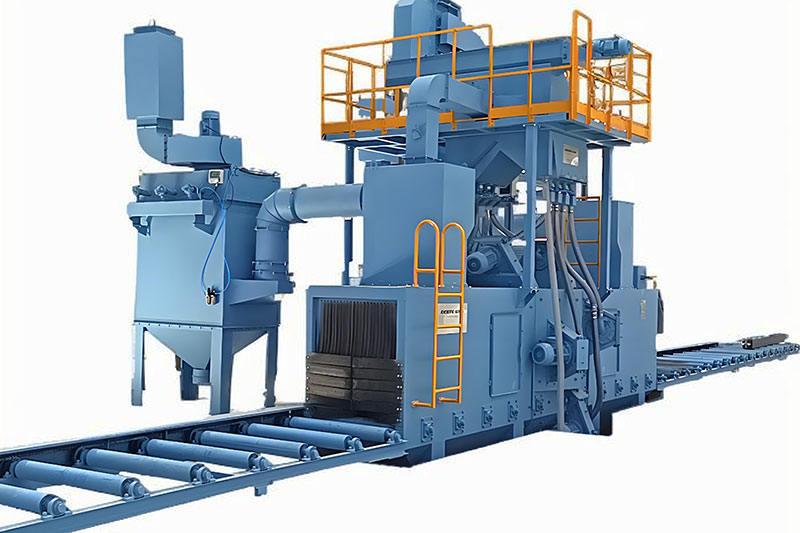
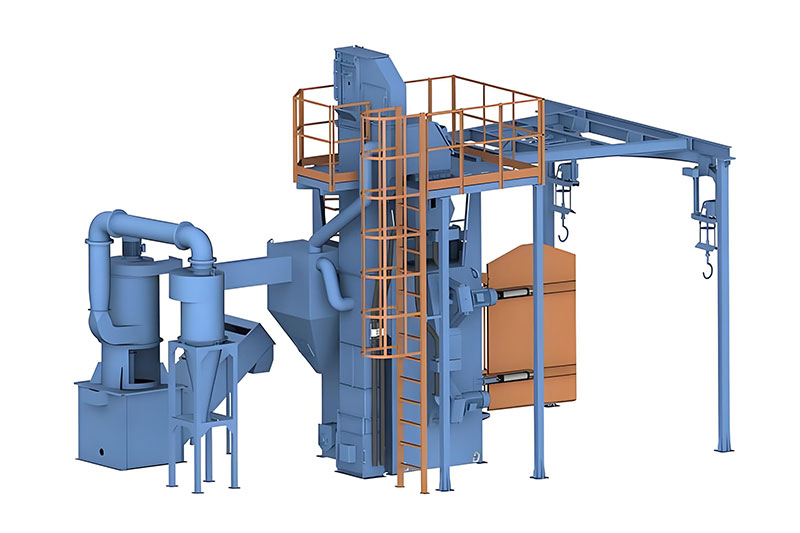
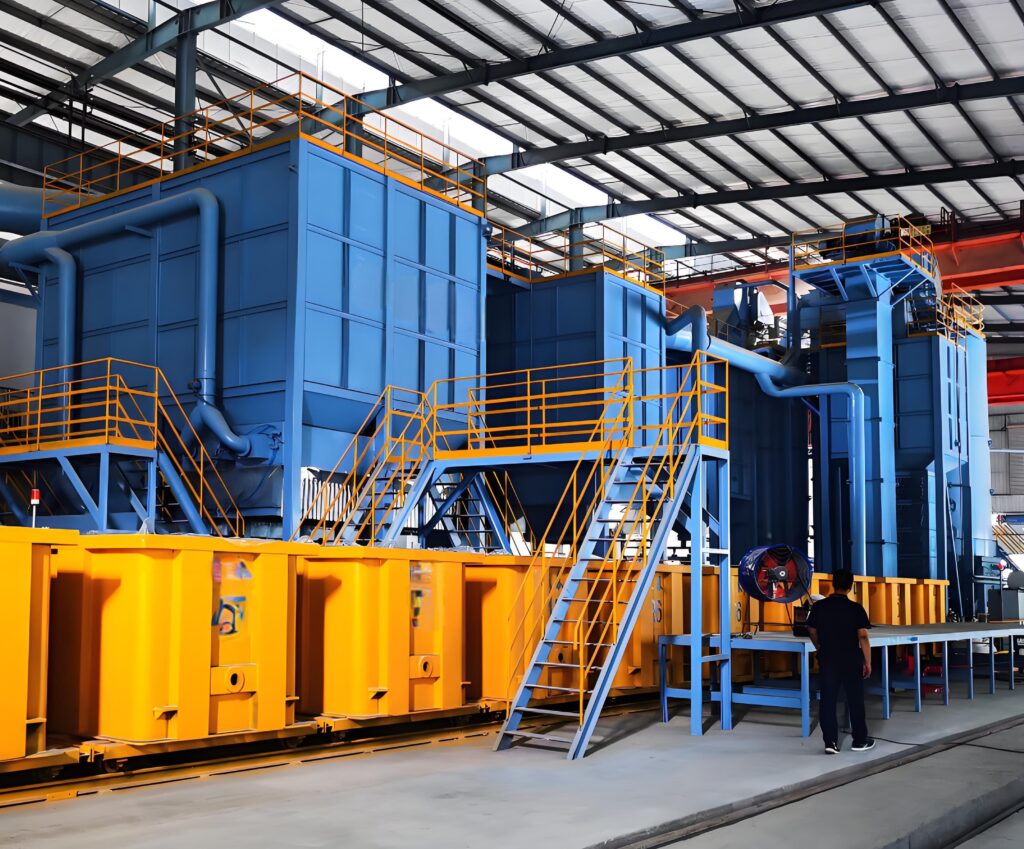
Understanding Shot Blaster Types is foundational to matching equipment with industrial needs. Tumblast machines are ideal for small, bulk workpieces like screws, gears, or stampings. Their rotating cylindrical drum tumbles parts, ensuring uniform contact with abrasive media—perfect for low-to-medium volume production in hardware or automotive parts industries. Track-type shot blasters use a rubber or steel track to convey medium-sized workpieces (e.g., castings, brake discs) through the blasting chamber. Equipped with multi-angle shot blasters, they balance efficiency and versatility, suiting batch production in foundries or auto component plants. Hook-type models feature suspended, rotating hooks that hold large, heavy workpieces such as steel beams, engine blocks, or hull segments. This design eliminates cleaning dead ends, making them indispensable in steel structure, shipbuilding, or heavy machinery industries. Through-type shot blasters are tailored for long workpieces like profiles, plates, or pipes, enabling continuous processing for high-volume assembly lines in construction steel or aerospace sectors. Each type is engineered for specific workpiece sizes, weights, and production demands, so identifying your use case is the first step to effective selection.

What critical selection tips ensure you pick the right shot blaster?
Mastering Selection Tips is key to avoiding costly mismatches. Start by analyzing workpiece characteristics: size, weight, material, and surface contamination level. For delicate aluminum parts, a tumblast machine with fine abrasive media prevents damage, while heavy steel components require the power of a hook-type model. Next, assess production volume: high-volume operations benefit from through-type or track-type machines for continuous processing, while small-batch workshops thrive with compact tumblast or tabletop models. Consider site constraints: hook-type machines need ample vertical space (minimum 5 meters ceiling height), while track-type models require more floor space for conveyor systems. Don’t overlook environmental compliance—choose machines with efficient dust collection systems (99%+ separation rate) and noise reduction features (below 85dB) to meet regulations. Finally, prioritize manufacturers with reliable after-sales support and readily available spare parts, as this impacts long-term operational efficiency. By aligning these factors with your needs, you select a shot blaster that delivers optimal performance and value.

What pro tricks maximize shot blaster efficiency and cleaning quality?
Implementing Efficiency Tricks elevates both productivity and cleaning results. First, optimize abrasive media selection: use harder media (e.g., steel shot) for tough materials like cast iron, and softer options (e.g., glass beads) for delicate surfaces. Regularly check media size—worn or oversized media reduces cleaning power, so replace it when it falls below the recommended diameter. Adjust blasting parameters (shot speed, angle, and intensity) based on workpiece requirements: increase intensity for heavily rusted parts, and reduce it for thin or fragile components. Invest in automation features like PLC control systems to ensure consistent processing, especially for high-volume production. Regularly clean the blasting chamber and dust collection system to prevent clogs, which hinder airflow and reduce efficiency. Additionally, schedule preventive maintenance for shot blasters—lubricate rotating parts, inspect nozzles for wear, and calibrate sensors—to avoid unexpected downtime. These tricks not only boost cleaning quality (e.g., achieving Sa2.5-Sa3 surface cleanliness) but also reduce operational costs by minimizing waste and maximizing throughput.
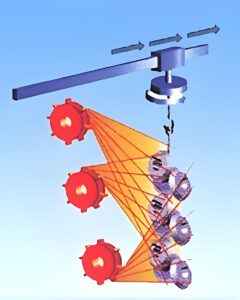
How to avoid common shot blaster operation and maintenance mistakes?
Avoiding pitfalls requires leveraging Maintenance Hacks and best practices. A common operational mistake is overloading the machine—this leads to uneven cleaning, increased wear on components, and reduced efficiency. Follow the manufacturer’s recommended workpiece capacity to ensure optimal performance. Another error is neglecting abrasive media quality: using contaminated or incorrect media causes surface damage, inconsistent cleaning, and premature wear on the machine’s liners and nozzles. Regularly sieve and replace media to maintain its effectiveness. On the maintenance front, skipping routine inspections is a critical misstep. Failure to check for loose bolts, worn liners, or clogged dust filters can lead to costly breakdowns. Clean the machine after each shift to remove debris and prevent corrosion, and lubricate moving parts (hooks, tracks, conveyor systems) at recommended intervals. Avoid using harsh chemicals for cleaning, as they can damage the machine’s finish and components. Additionally, train operators on proper use—untrained staff may misuse controls, leading to inefficient operation or safety hazards. By addressing these common mistakes, you ensure smooth, reliable performance.

What factors extend the service life of your shot blaster?
Prioritizing Service Life Extension requires a proactive approach to care and use. First, invest in high-quality, wear-resistant components: choose machines with manganese steel liners, high-chromium blades, and durable rubber tracks, as these parts withstand the abrasive nature of the process. Regular maintenance is non-negotiable—schedule weekly inspections of nozzles, liners, and abrasive recycling systems, and replace worn parts promptly. Proper storage and environment also matter: keep the machine in a dry, well-ventilated area to prevent rust and corrosion, and protect it from extreme temperatures or humidity. Use abrasive media as recommended by the manufacturer—using the wrong type or size accelerates component wear. Avoid overworking the machine; allow for cool-down periods during long production runs to prevent overheating. Additionally, partner with a manufacturer that offers comprehensive after-sales support, including technical assistance and spare parts availability. By combining quality components, regular maintenance, and proper use, you can extend your shot blaster’s service life by 30-50%, maximizing your investment.
Conclusion
This guide simplifies shot blasters—master types, tips, and hacks for long-lasting, efficient performance.